Application Security
Applications are constantly changing with Operating System (OS) updates, bug fixes and new features. Cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated every day making it increasingly difficult to secure our applications.
Application security ensures the confidentiality, integrity and availability of the application and sensitive data within, by preventing security breaches and protection against cyber-attacks.
75%
of organisations believe that application security is a top
priority, but only 35% have the resources to address it.
Source – Ponemon Institute 2022 State of Application Security Survey
How it works
The application security process involves applying measures that can identify new or abnormal code, detect whether it’s vulnerable, and action a fix before being exposed to a breach or attack.
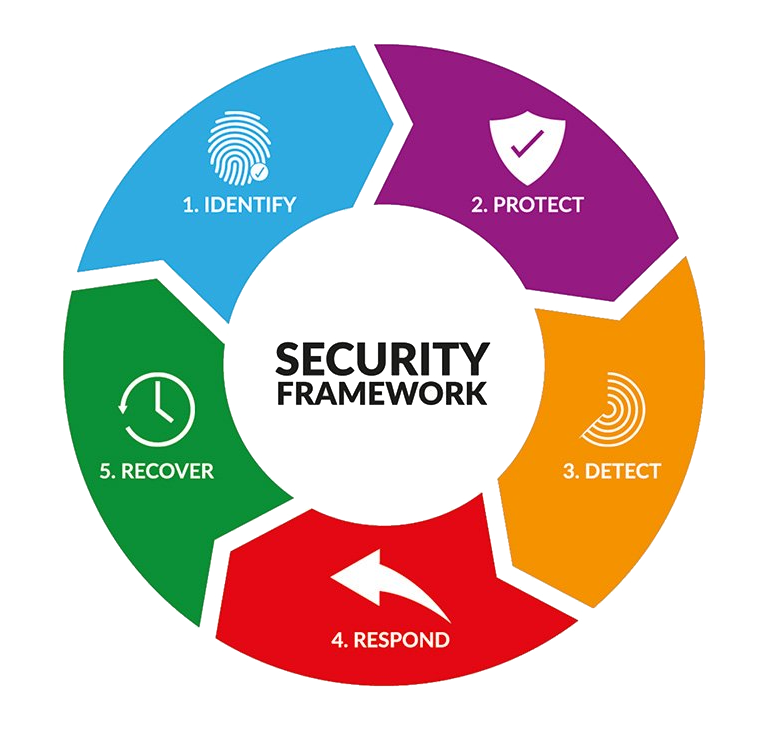
- Identify – Find security risks before those risks become a bigger problem.
- Protect– By security testing and applying the right tools to safeguard your code.
- Detect – Integrate tools to find and alert you to threats and vulnerabilities.
- Respond – Take the necessary action to stop or minimise any flaws, vulnerabilities or threats when they have been detected.
- Recover – Fix any issues that arise and restoring regular operational capabilities.
Why it’s important
Protect against data breaches & cyber-attacks
Prevent significant financial loss or damage to reputation. Application security helps protect sensitive data from theft or unauthorised access. By identifying and mitigating potential security risks in applications reduces the risk of data breaches.
Reduce downtime
Application security helps ensure that applications are available and functioning properly, reducing the risk of costly downtime that can negatively impact productivity, revenue, and customer satisfaction.
Increase customer confidence
Demonstrating a commitment to application security can help increase customer confidence in the ability to protect their sensitive information. This can be particularly important for organisations that handle sensitive customer data, such as financial institutions or healthcare providers.
Maintain regulatory compliance
Many industries are subject to regulations that require them to maintain certain security standards. Application security can help ensure compliance with these regulations by addressing security risks that could lead to a compliance violation.
Avoid being part of a statistic
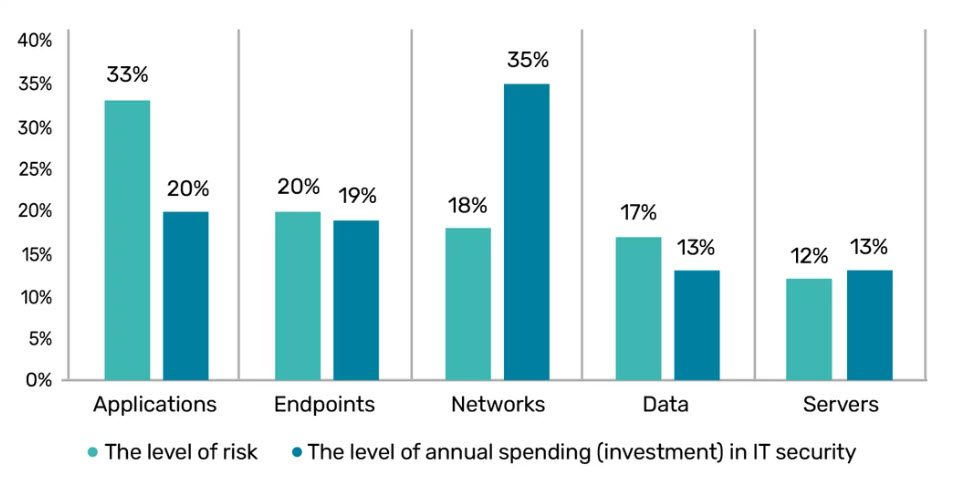
70% of organisations have experienced at least one data breach due to insecure applications. *
The level of risk within your ecosystem should be considered when deciding on how much investment you allocate per area. The higher the risk, the more you should be prioritising to protect your business.
Attacking application vulnerabilities is one of the most common cyber-attack methods for hackers. Despite this, many applications remain unprotected with minimal security solutions implemented through the lifecycle and beyond.
With our vendors, Climb Channel Solutions provide an extensive range of tools to protect your application through its full lifespan.
*Source: Ponemon Institute

Back up and recovery
Unlock the safety net for your customers. Safeguarding data with our proactive backup and seamless recovery solutions.
Protect your data and ensure business continuity with our reliable and efficient backup and recovery solutions. With our vendors, we offer a comprehensive set of tools and solutions designed to significantly reduce the risks of data loss and facilitate fast and simple to action recovery options.
70%
of organisations will suffer business disruption due to data loss. How fast you can recover your data in those situations depends on the robustness of your backup solution.
Source – https://www.mtechusa.us/social-engineering-prevention/the-impact-of-data-loss-on-business/
What are the greatest
risks to data?
Ever accidentally pressed the delete button
It can be this easy to lose valuable data, but by having a backup solution in place you can get it back! Without a backup solution, you could accidentally press delete and lose that data forever.
Your computer breaks with everything is saved locally
Creating backups on a remote cloud solution allows you to recover this data to another desktop.
Cybercriminals – Ransomware attacks
Ransomware blocks end-users from accessing files and applications, and hackers will demand a ransom to restore the access. By having a backup procedure in place, you have peace of mind that you have alternative areas to access your valuable data.

Be ready to recover – just in case
In a study conducted by ESG, 81% of Microsoft Office 365 users had to recover data, but only 15% were able to recover 100% of their data.
Minimise data loss
In the event of system failures, breaches or other unforeseen circumstances, have the peace of mind your data is safe and can be restored from the last safe state.
Customer Satisfaction
It’s become an expectation that applications and services ensure uninterrupted access. Enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty with a robust recovery method.
Reduce downtime
A recovery method allows for a quick and simple restoration. Significantly reduce the time your services are down and ensure optimum operation time for your business.
Reliable replication
Replication allows you to essentially rewind your progress and start again in case of a data loss. Replication functionality is the quickest way to retrieve data and save time on the recovery process without causing any backlog in business processes.
Regulatory compliance
Many industries have strict regulatory requirements regarding data protection and availability. Implementing a recovery method ensures you can demonstrate your ability to restore data and maintain system integrity.
Save money
The financial impact includes lost productivity, potential revenue loss, and expenses associated with data recovery. Avoid expensive data recovery services or time costing manual intervention with a reliable recovery solution

Why is cloud security important?
Many businesses have migrated their data to the cloud and while third-party software takes on the management of the infrastructure, keeping the information secure doesn’t always fall to them. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, security threats are becoming more advanced and many of these are now targeting cloud computing providers. If an organisation does not have a cloud security solution, it could face government and compliance risks when managing client information.
80%
of companies have experienced at least
one cloud security incident in the last year.
Source – expertinsights.com
Types of Cloud Security
IAM
Deploy policy-driven enforcement protocols for users wanting to access cloud-based services.
Data Loss Prevention
Tools and services to help organisations ensure the security of regulated cloud data.
SIEM
Automate threat monitoring, detection, and response in cloud-based environments.
Disaster Recovery
Have the tools, services and protocols to expedite the recovery of lost data and resume business as usual.
Cloud Security Challenges
Multitenancy
Public cloud environments house multiple clients under the same umbrella. If your customers are using a public cloud environment it is possible their hosted devices will be compromised by malicious attackers even if they were targeting another business.
Access Management
Managing and restricting access points in cloud environments can be challenging compared to on-premises systems. If organisations do not have a bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policy, this can be dangerous as it allows unfiltered access from any device or geolocation.
Compliance
When it comes to public or hybrid cloud deployments, compliance management can often be a source of confusion. Accountability for data privacy sits with the organisation but if they heavily rely on a third-party solution, it could lead to costly compliance issues.
Misconfigurations
Misconfigured assets accounted for 86% of breached records in 2019 (source: IBM). This has become a key issue for cloud computing environments. A misconfiguration can be saving default administrative passwords or not creating the appropriate privacy settings.

What is endpoint management?
Endpoint management is an important security feature for all businesses as it authenticates and supervises access rights of endpoint devices and networks. Endpoints can be anything from employee laptops, desktops and tablets to on-premises servers and applications running in the cloud. As remote working and cloud infrastructures take over from what we once knew, the work of security teams has changed.
$3.86M
The average cost of a data breach in 2020.
Endpoint breaches accounted for 29% of the total.
Source – IBM
Types of Endpoint Management
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
IT administrators can control, security and enforce policies on company owned smartphones, tablets and other endpoints. MDM can protect corporate networks while optimising functionality and security of mobile devices.
Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM)
EMM can be used to manage company-owned and person devices under the bring your own device (BYOD) policy. It also improves security and productivity by increasing the range of devices companies can offer.
Unified Endpoint Management (UEM)
UEM allows you to secure and manage multiple devices from a single console. This includes pushing updates to devices, applying security policies or remote wiping for lost/stolen devices.

Top tips for endpoint management
Identify devices
Security teams need to keep an inventory of endpoints so they can monitor them in real time and ensure all are kept secured.
Patch management
Patches have always been an important part of securing endpoints, but software vulnerabilities are being exploited by attackers, so organisations need to make sure patches are applied promptly.
Analyse endpoints
When an attack happens, IT teams need to be able to respond immediately. It’s important for organisations to have a system in place analysing endpoints at all times, so they can see what has happened and what threats remain active.
What is firewalls and network security?
Network security is any activity designed to protect the integrity of the network; it targets a variety of threats and it stops threats from spreading around the network. A firewall is a network security device monitoring incoming and outgoing traffic. Its purpose is to block any potential threats and malicious attacks like a virus or hackers.
Benefits of Firewalls
Monitors network traffic
Firewalls will monitor all incoming and outgoing data and block any potential threats and attacks.
Stops virus attacks
Virus attacks can cost businesses huge amounts if they aren’t caught in enough time. Firewalls can control the entry points of your device meaning they can shut down attacks as soon as they’re found
Prevents hacking
Businesses are moving towards digital operations and naturally this invites hackers to follow the same path. Data theft is on the rise, so now more than ever firewalls are important to prevent this access.
Stops spyware
One of the most common ways hackers gain access to devices is through spyware and malware. These attacks can give full access of the device to the hackers, by using firewalls you can block these attacks from happening.
7 common network security issues
Internal security threats
Internal actions can have a negative impact on business’ networks resulting in downtime, loss of revenue and loss of trust from customers.
Distributed Denial-Of-Service (DDoS) attacks
Cybercriminals infect mobiles, computers and other internet-connected devices and convert them into bots. From here the hackers send the bots to a victim’s IP address, causing the website to crash and malfunction.
Rogue security software
Rogue security software tricks businesses into thinking their IT infrastructure isn’t operational due to a virus. The device is infected with malware and the user receives messaging forcing them to pay for a security solution that is non-existent.
Malware
Malware is used to gain information about victims through compromised devices. Hackers can search for classified information which they can then use to commit identity theft, blackmail and more.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files and holds them for ransom. Victims are forced to pay for this to receive the decryption key to unlock data.
Phishing attacks
Phishing attacks can take the form of emails, text messages, or phone calls. Hackers disguise themselves as a trusted entity and attempt to gain access to networks and steal personal information.
Viruses
Viruses tend to be attached to downloadable files from emails or websites. Once the file is opened the virus exploits vulnerabilities in the software to disrupt network traffic, steal data and more.
Why work with Climb?
Climb Channel Solutions works with a wide range of vendors that offer security solutions .
Our team of experts can help you get the right solutions for your customers to secure their apps, cloud, endpoint and more.
Get in touch with the team today by filling in the form or giving us a call on +44 (0) 1364 655 200
By submitting this form you are agreeing to our Privacy Policy and Website Terms of Use.

